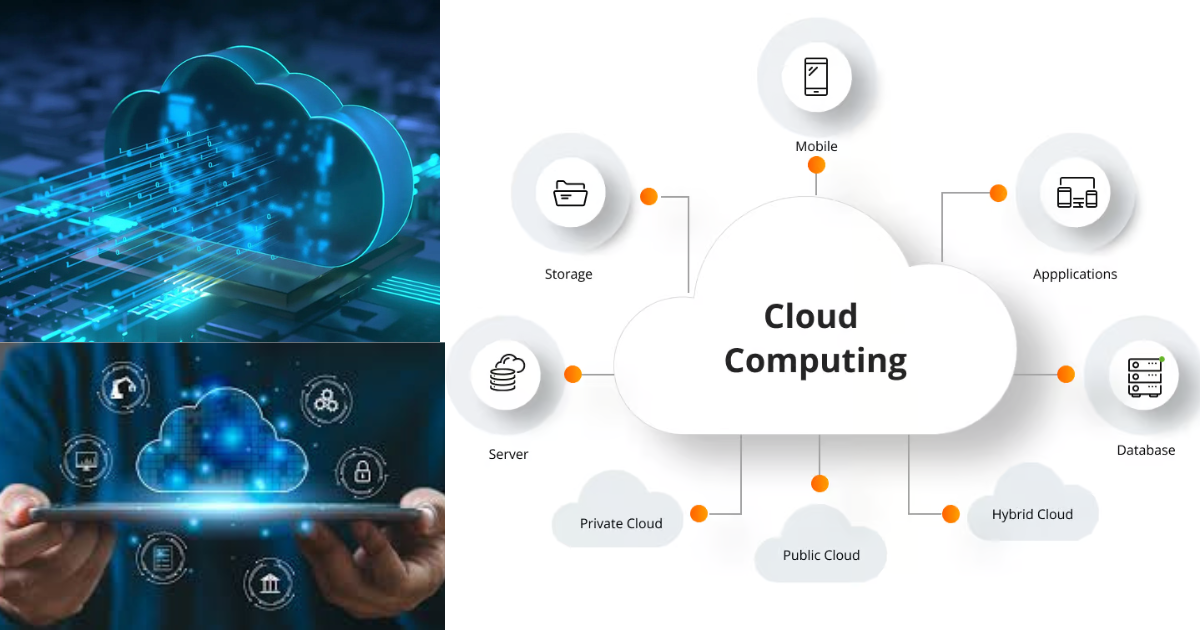
How Cloud Computing is Revolutionizing Technology and Business Cloud computing refers to the provision of computing capabilities (servers, storage and databases, networking and software) by the internet rather than using the local computer hardware. It is flexible, cost-effective, and scalable to both individuals and business since it offers on-demand access which is based on pay-as-you-go. Cloud services are used in our everyday digital lives, whether to stream movies and check emails or to run applications created and driven by AI.
Cloud computing and its services

The following are the most popular cloud computing service models:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service: provides a variety of virtual services, including servers, storage, and networks.
PaaS ( Platform as a service): Provides an innovative platform for develop, test, and launch applications.
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service): This is the fulfilled services of applications by the internet without any installation or maintenance.
Serverless Computing: It follows an automatically managed backend infrastructure, giving the developers the opportunity to write only codes. These services can be divided into various segments as we will discuss in the sections below how cloud computing is still transforming technology and business. How Cloud Computing is Revolutionizing Technology and Business
How cloud computing services are changing the IT landscape

Cloud computing has ceased to be a futuristic concept, it is now the foundation of the new IT. Its use was only speeded up by the pandemic, as companies across the globe needed to find methods of ensuring that employees could remain connected, that data was secure and businesses could operate in a way that was not impacted by the pandemic. How Cloud Computing is Revolutionizing Technology and Business Starting as a temporary workaround to remote working, it has now become a worldwide transformation of the way technology is provided and consumed. The cloud today is not merely a substitute to traditional infrastructures but the basis of flexibility, scalability and innovation in industries.
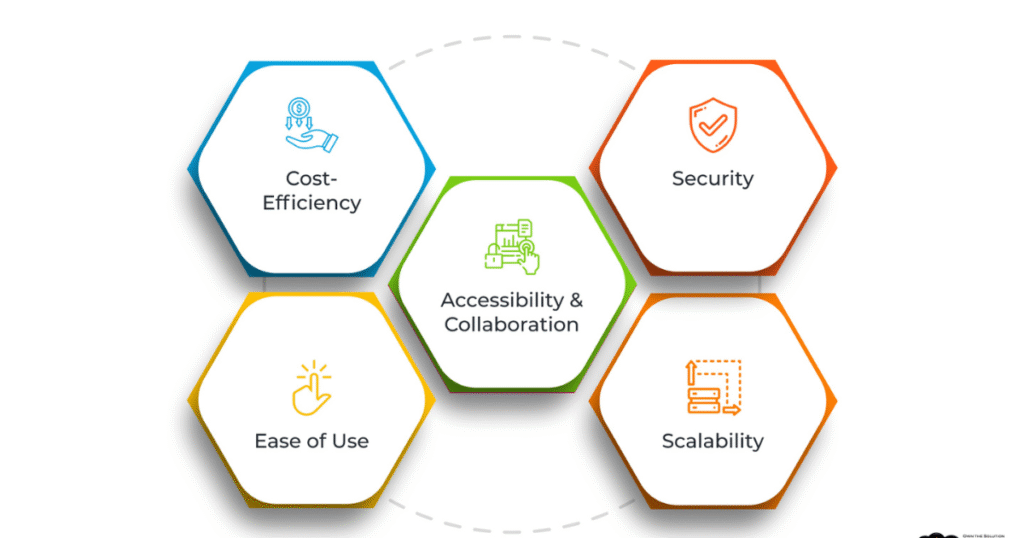
1. Availability and Cooperation.
The way in which cloud computing dismantles the geographical barriers is one of the biggest contributions of cloud computing. Through an internet connection employees are able to work together in real time, share documents with ease and access an application anywhere. This has remodeled team work, whereby remote work and hybrid work models are not only feasible, but also more productive.
2. Flexibility and Scalability.
Conventional IT systems were accused of not being able to handle variable workloads and were also expensive to upgrade in terms of hardware. On-demand scalability is the solution to this issue provided by cloud computing. Organizations are able to increase or decrease resources at any given moment which ensures efficiency in times of high demand and cost saving in times of low demand.
3. Cost Efficiency
Cloud services minimize the cost of having costly infrastructure, software licenses and maintenance employees. Businesses do not need to purchase hardware but just pay the resources utilized. The pay as you go model has created a level playing field whereby startups and small business enterprises can access enterprise grade technology.
4. Creativity and Testing.
The cloud provides a risk-free setting for testing. Businesses may rapidly create applications, run trials, and iterate without having to make large capital commitments. This flexibility promotes machine learning, analytics, and artificial intelligence in addition to helping companies stay ahead of the curve and change more quickly.
5. Improved Data protection and compliance.
The issue of security is a leading concern in the area of IT, and cloud providers have created sophisticated security measures, like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and real-time monitoring. Others are also in line with such international practices as GDPR and HIPAA providing organizations with the assurance to process sensitive data and mitigate regulatory compliance needs.
6. Disaster Recovery and Business continuity.
Cloud solutions help businesses stay up and running by keeping data safe across multiple locations. Even if something goes wrong, automatic backups and failover systems make recovery quick and smooth, reducing downtime and preventing major data loss.
7. Big Data and Advanced Analytics.
Cloud computing platforms also make companies handle large amounts of data and analyze them without having to install a supercomputer. Premier services such as Google BigQuery and Amazon EMR enable IT departments to unlock insights, predictive analytics, and integrate AI into operational workflows to unlock smart decision-making at scale.
8. Global Expansion
Cloud providers enable companies to introduce services in new locations near real-time as they have data centres around the globe. Not only does this decrease latency to customers but also makes expansion into international markets by organizations occurs effortlessly.
9. Sustainable IT Practices
Cloud also helps to make the environment sustainable. Data centres are more efficiently run compared to the on-premises systems, which are usually fed on renewable energy that is spread across various points. Moving to the cloud saves businesses on energy waste and overall carbon-footprint.
10. Challenges to Consider
Although the advantages are enormous, there are issues associated with cloud adoption. Vendor lock-in, privacy issues, and complexities of compliance is a challenge to several organizations. Nevertheless, the risks can be reduced with the proper strategies and selection of the providers.
Database as a Service (DBaaS) in cloud computing
What is DBaaS?
Database as a Service (DBaaS) is a type of cloud computing where users can access and maintain databases without having to worry about the details of hardware installation, software configuration, or maintenance. In this model, the cloud provider will handle setup, updates, scaling, and security- businesses will just use the database to handle their applications.
Additionally, DBaaS offers a pay-as-you-go model in place of costly upfront infrastructure investments, which is especially attractive to startups, SMBs, and enterprises that require agility.
Key Benefits of DBaaS
Cost Efficiency
Conventional databases are costly in terms of server cost, upgrades, and energy. Under DBaaS, businesses pay based on consumption of services- there is no wasted resources no excessive amount spent on capacity in the future.
Scalability on Demand
Databases can be increased or decreased in no time. Have to store more, when sales are at their peak? Add it in minutes. Low usage? Scale down and save money.
Simplified Management
To have a database on the premises requires a complete IT department. DBaaS leaves this task to the vendor and allows the internal employees to focus on innovation instead of regular administration.
Faster Development
Developers no longer wait to have an IT approval. DBaaS helps them to launch a new database within a few minutes, faster time-to-market.
Enhanced Security
The major providers guarantee encryption of the data, the permissions, and the compliance regulations to preserve the sensitive data.
Reduced Downtime Risks
Cloud providers tend to support their DBaaS using SLAs that assure uptime. In case of downtime, the businesses are relieved, and risk is reduced.
Benefits Compared to Traditional Databases.
No servers to purchase or maintain.
Reduce infrastructure and power expenses.
Quick implementation of the solution versus weeks of on-premises implementation.
In-built strength to expand businesses.
Potential DBaaS Cons.
DBaaS is admittedly not without its issues, although it has numerous benefits:
Less Control: Organizations do not have direct control of the infrastructure.
Vendor Dependence: failure at the provider side results in downtime to the users.
Security Concerns: The industries that have stringent rules might not be willing to save vital information on the cloud.
Latency Problems: Sometimes, when it involves the large scale transfer of data over the internet, it can slack performance.
DBaaS Providers to Consider
DBaaS is available on most of the large cloud platforms today. Others that are popular are:
Amazon DynamoDB – The fully-managed NoSQL service with high performance and easy scaling.
Google Cloud SQL – MySQL and postgre SQL databases that are managed and come with features of developer friendliness.
Oracle Database Cloud- Intense relational database system with multimodals.
MongoDB Atlas MongoDB is an elastic NoSQL database designed to support the demands of the modern application.
Azure SQL Database This Microsoft relational DBaaS is based on SQL server.
IBM Db2 – Excellent in the real-time analytics and high load.
SAP Business Technology Platform – Cloud and hybrid environment and integrated platform.
DigitalOcean Managed Databases- Light and reliable to developers and SMBs.
Who Should Use DBaaS?
Small & Medium Businesses (SMBs): Does not invest heavily in IT.
Enterprises: Makes large scale database management easier.
Developers & Startups: Provides prototyping fast and launches apps swiftly.
Nevertheless, enterprises that handle the workloads that are highly sensitive or mission-critical might still choose the hybrid or on-premises configurations.
Google cloud computing services

Google Cloud Platform (GCP) refers to a family of cloud computing services offered by Google to assist businesses, application developers, and enterprises to create, operate, and expand applications without the concern of underlying physical infrastructures. How Cloud Computing is Revolutionizing Technology and Business GCP offers flexibility, security, and performance, and is useful to deploy Web sites and databases as well as drive artificial intelligence (AI) models.
The distinctive feature of GCP is a presence of a worldwide network of data centers, effective security measures, and smooth integration with other popular Google applications such as Gmail, Google drive, and YouTube.
Google cloud platform has several important features.
Global Infrastructure
Operates on the same backbone network as Google Search, Gmail, and YouTube, and is fast and reliable all over the world.
Wide Range of Services
offers services for computing, networking, storage, IoT, AI, machine learning, and data analytics.
Strong Security
Inbuilt services such as Identity and access management (IAM), Key Management Service (KMS) and security command center are used to safeguard data.
Developer-Friendly Tools
GCP provides ready-to-use tools that accelerate innovation since it contains BigQuery, an analytics tool, and TensorFlow, an AI tool.
Scalability & Flexibility
Start local and go global GCP can accommodate your business requirements.
The interaction with Google cloud services.
Google cloud offers three primary access and managements of its services:
Google Cloud Console
An easy to use web interface used to set up and track projects.
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Through the gcloud CLI (Cloud SDK or Cloud Shell) developers will be able to run services directly in a terminal.
Client Libraries
Language APIs such as Python, Java and Node.js which help in integrating GCP more easily into applications.
GCP vs. Google Cloud
Google Cloud and GCP (Google Cloud Platform) are mixed up. Here’s the difference:
Google Cloud = Everything that Google provides under the cloud (Google Workspace, Android Enterprise, Chrome OS, and APIs).GCP = The core cloud infrastructure services (such as: App Engine, BigQuery, Compute Engine, etc.) that it offers in its pricing models.
In short, GCP is one of the parts of a larger Google Cloud system.
Pros and Cons of GCP
Advantages
Extensive Service Portfolio: Includes all of computing and storage to AI and analytics.
Global Reach: Takes advantage of the strong global infrastructure of Google.
Innovation: quick adoption of new technologies, especially AI/ML.
Grade-level security: In-built IAM, encryption and compliance.
Disadvantages
Complicated Pricing: There is no guarantee of cost determinability by new users.
Support Limitations: Some users complain that the support is slow or limited when compared to the competitors.
Vendor Lock-In: Since it is a proprietary platform, it may be hard to move to another service.
Why Businesses Choose GCP
Startups: Cheap entry point and free credits.
Businesses: Intelligent analytics, AI, and global intelligence.
Developers: Automation, malleability, and convenience.
GCP lowers expenses, boosts productivity, and spurs creativity in both Fortune 500 businesses and small teams.
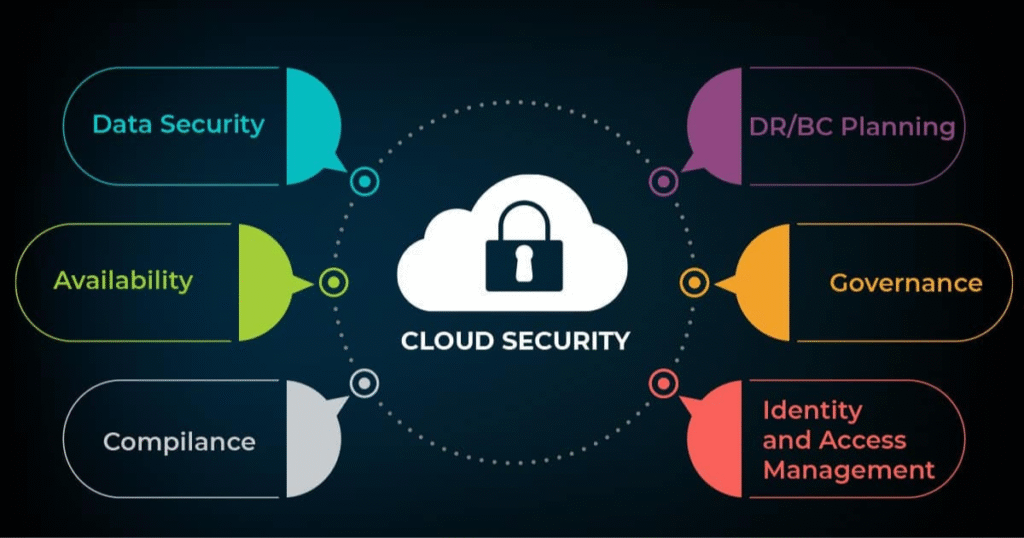
Security as a service in cloud computing
Security as a Service (SECaaS), is the cloud-based security solution that provides security services to businesses in subscription format. To protect, improve, and maintain their networks, organizations may also contract specialized services to support their cybersecurity demands but not to buy costly equipment or license. This will save on expenses, simplify operations and allow businesses to constantly utilize the latest security tools.
How SECaaS Works
In the past, antivirus software, firewalls and spam filters were installed on individual computers or servers, and they had to be updated on a regular basis, at considerable expense. Under SECaaS, such tools are stored in the cloud and they are provided as services.With this model, there is no initial hardware costs, and intricate license renewal procedures. Rather, companies are paying to have scalable security solutions that can be modified as the threats change.
Core Components of SECaaS
Encryption -Secures data, this is information that is incomprehensible without the necessary authorization. Network Security -observes and regulates access to network service Email Security -Protects phishing, spam, and malware in emails. Identity Management -Makes sure that only legitimate users are allowed in.Data Loss Prevention (DLP) – This is used to prevent unauthorized access or leaking sensitive data. Threat Intelligence & Monitoring -Identifies and acts upon cyber threats on the fly.How Cloud Computing is Revolutionizing Technology and Business
Benefits of SECaaS
Cost-Effective: Do not have to purchase new hardware or deal with licenses: just pay as you consume.
Virginity: Producers constantly update the tools such as antivirus and intrusion detection tools.
Leveraging Expertise: Ready-to-hire cybersecurity experts without the need to recruit a complete in-house team.
Scalability: Protective expansions are easily scaled up as the organization expands.
Swift Implementation: The services are provided in real time through the cloud.
Communication: Web dashboards allow IT teams to see into threats and security actions.
Resilience Against Attacks: 24/7 monitoring of systems to spot and mitigate such attacks as DDoS or malware.
Challenges and Limitations
Although SECaaS has its benefits, it has some possible limitations:
Less Control:With security being outsourced the businesses do not have a lot of control over the underlying infrastructure.
Shared risks: On-demand services that are provided through clouds may make organizations vulnerable to risk in case the host is affected by an attack.
Vendor Dependency: SECaaS service provider goes offline, there is a risk of security services being affected temporarily.
Complexity in Choice: Not every provider is suitable to the company-specific compliance or security requirements.
Selecting the SECaaS Provider.
Organizations must consider the following when choosing a SECaaS vendor:
24/7 support teams and quick response teams.
Adaptable and custom-made solutions to business needs.
Established history of dealing with enterprise level security.
Extensive cloud coverage, endpoint coverage and workload coverage.
Good compliance and data protection.
Actual SECaaS in the Real World.
Automated Threat Detection: The malware is detected and eliminated before it can spread.
Spam & Virus Filters: It prevents bad emails before they can get into the hands of the users.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Warns a business about intrusion attempts.
Continuous Monitoring: Monitoring suspicious activity and responds in real-time.
What is the effect of cloud computing on the IT industry?
Cloud computing is changing IT as it is scalable, cost effective, easily accessible remotely, more secure, and quicker to innovate with. It has turned out to be the support of the modern digital infrastructure.
What would be the role of Google cloud in cloud computing?
Google Cloud offers worldwide infrastructure and services like storage, databases, AI/ML, networking and BigQuery analytics. It assists the companies in expanding at a rapid pace, remaining safe and being efficient in innovation.
What is the significance of Database as a service (DBaaS)?
DBaaS is also easier to manage as it does not require manual database setup, management and scaling. It is cost saving, faster in development and is highly available and secure.
What are the benefits of the Security as a Service (SECaaS)?
SECaaS provides scalable, current and affordable security services including encryption, identity management and intrusion detection. It also does not need hardware installed on premises and also supports real-time threat monitoring.
Final Thoughts
Cloud computing has emerged as the core of the contemporary IT with features of flexibility, scalability and security based on models such as IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, DBaaS and SECaaS. Although it has its pitfalls, its advantages, including cost reduction, innovation, and accessibility worldwide, are necessary to all businesses that want to remain competitive in the digital age.How Cloud Computing is Revolutionizing Technology and Business